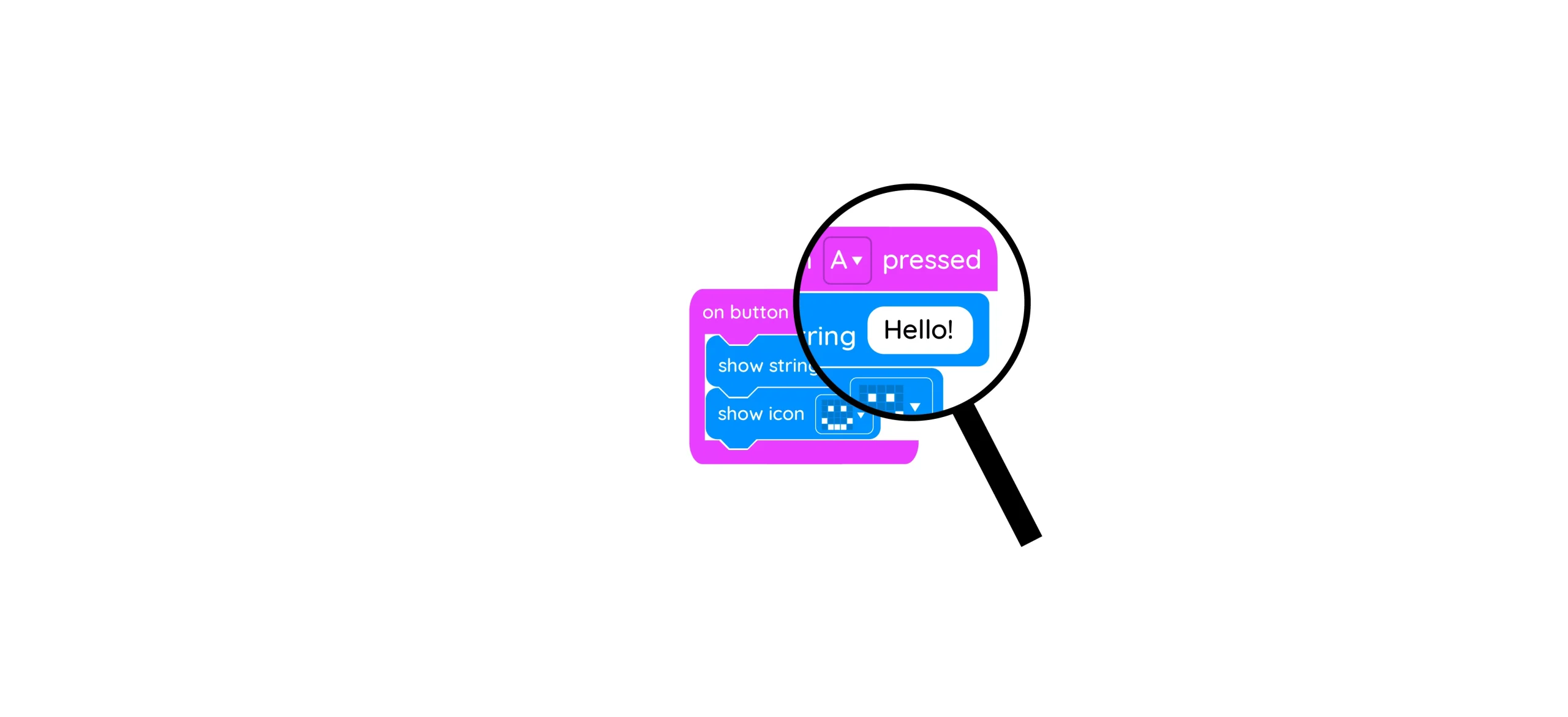
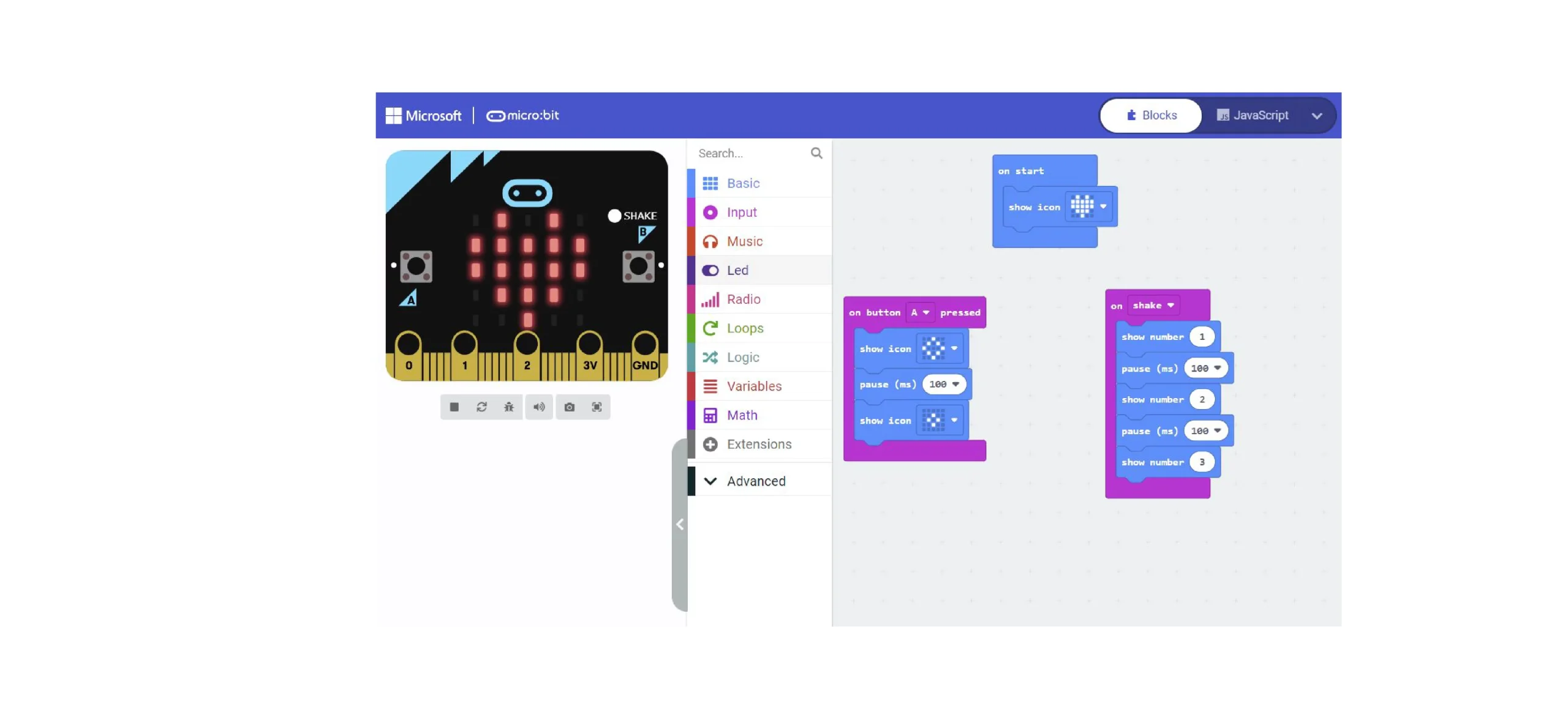
Learning intention
- To use code to solve problems.
Success criteria
- I can break a task down into smaller
We do not currently offer this subject
Cambridge Primary Computing (0059) Learning objectives
Computational Thinking
We do not currently offer this subject
Before the lesson
We do not currently offer this subject
Lesson plan
Recap and recall
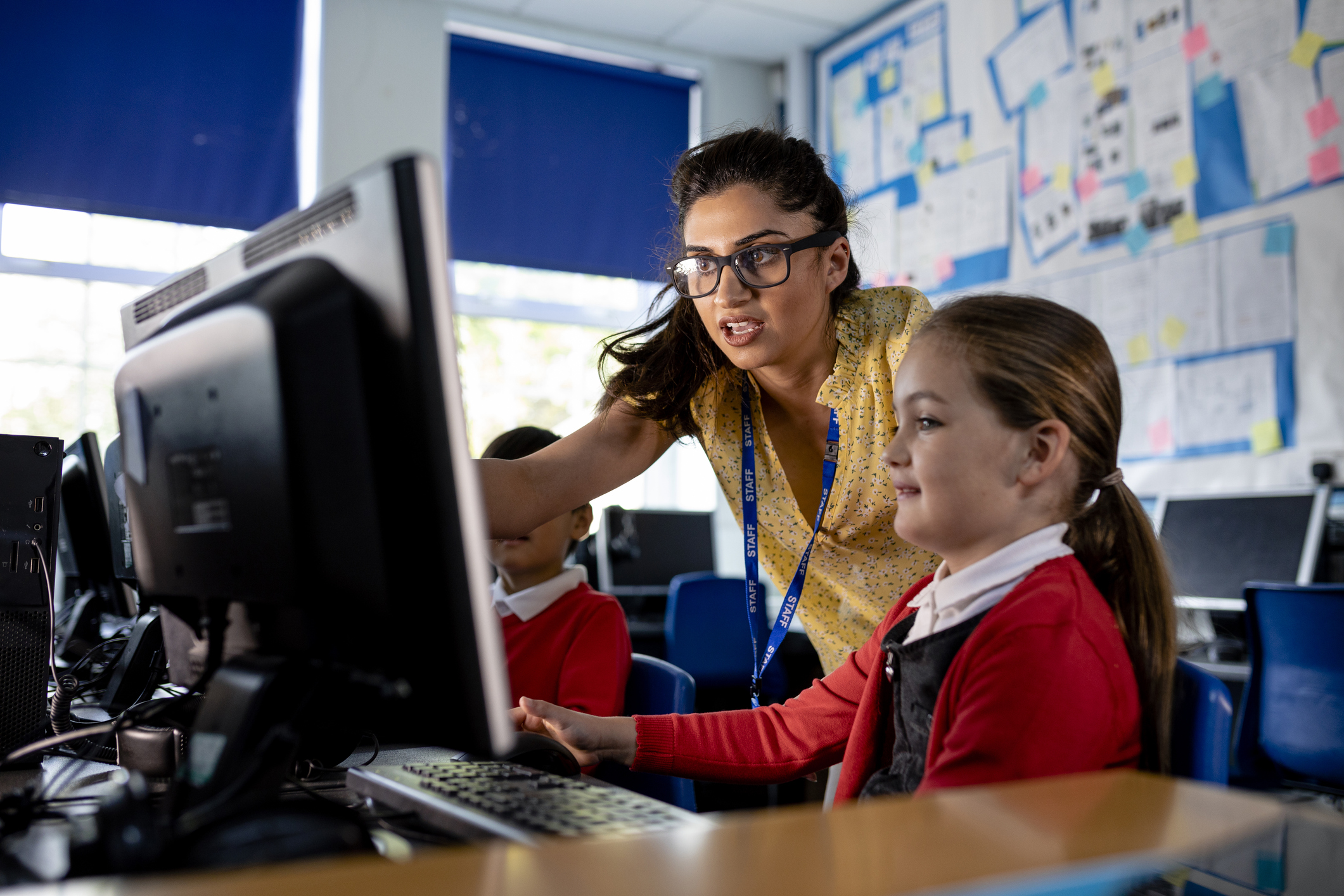
Tell learners to imagine that you are a robot and give instructions to help you move from one side of the classroom to another (for example, from the whiteboard to the door). Tell them you will only do exactly what they say. Ask for one instruction at a time. For example: Take one step forward.…
This content is for subscribers only. Join for access today.
Extended-mode explainer videos
How to extend your display to view the lesson page and preseantion mode simultaneously. Choose your operating system below to watch the video
If you need further support with extending your display,
please contact [email protected].
Differentiation
Learners needing support:
- Should say the instructions they are giving to the computer (for example, if they are using a forward arrow, they should say ‘go forward 1 square’).
- Could use a whiteboard to record each step as they build their algorithm.
Learners working at a stretch:
- Should explain how each step contributes to solving a problem.
- Could record each step they make in their own way.
We do not currently offer this subject
Assessing progress and understanding
Learners with secure understanding can:
- Recognise the small steps to solve a problem.
- Focus
We do not currently offer this subject
Vocabulary definitions
-
abstraction
Focusing on the important parts and ignoring the extra details.
-
algorithm
A set of steps to solve a problem or complete a task.
We do not currently offer this subject